Sustainable Textiles from Agro-Waste: Development and Performance Evaluation of Pineapple Leaf Fiber (PALF) Blended Yarns and 100% Cotton
Abstract
1, Ragib Mahbub 2, Md Kowsar Alam
3* ,Engr. Md. Abu
Sayed4
1Textile Engineering
College, Zorargonj, Chattogram
2Textile
Engineering College, Zorargonj, Chattogram
3Textile Engineering
College, Zorargonj, Chattogram
4Dept. of Yarn
Engineering, Textile Engineering College, Zorargonj, Chattogram
Corresponding author’s e-mail address: Kowsaralam017@gmail.com
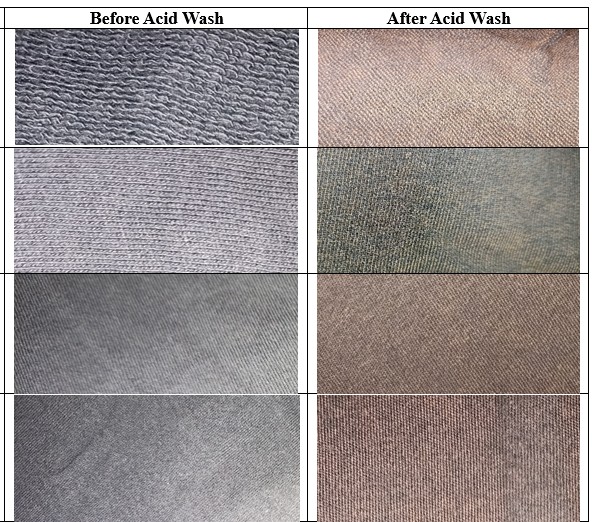
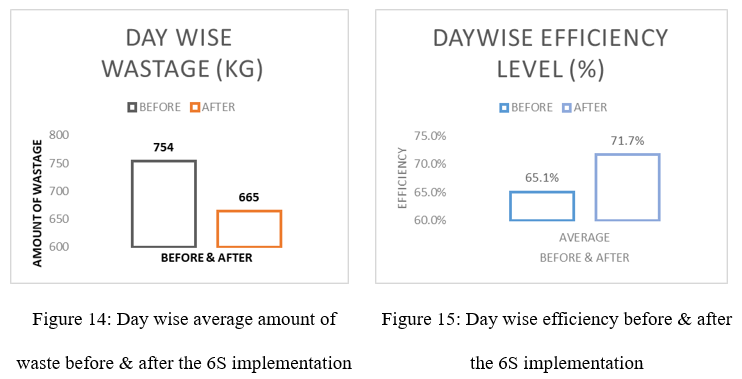
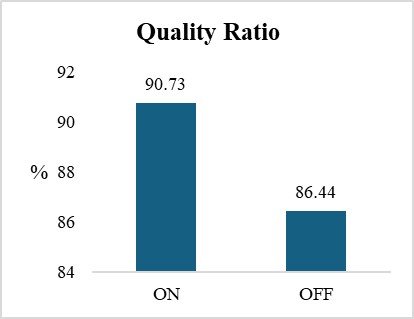
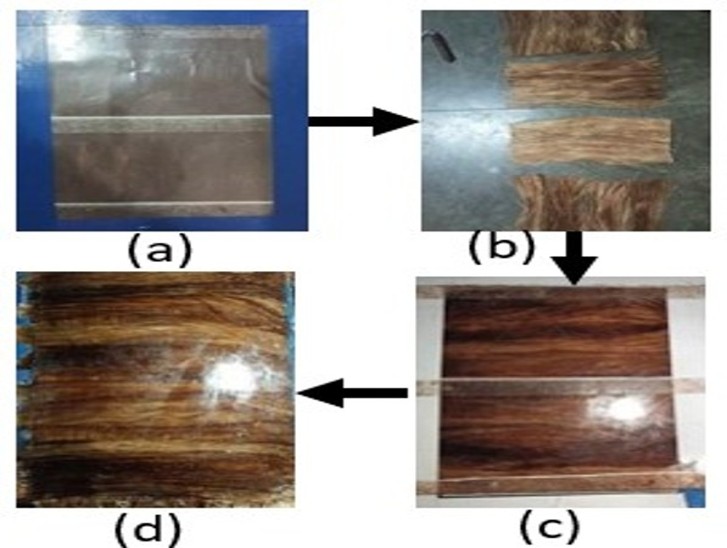
Rising global demand for sustainable textiles is driving attention toward innovative natural fibers, among which Pineapple Leaf Fiber (PALF) stands out for its exceptional tensile strength, natural luster, and complete biodegradability. In Bangladesh, where the spinning sector remains heavily reliant on costly cotton imports, Pineapple Leaf Fiber (PALF) presents a locally available, environmentally sustainable alternative with the potential to reduce import dependence, optimize the utilization of indigenous resources, and convert agricultural waste into value-added products. Pineapple cultivation produces abundant 3-ft leaves, often discarded or used as low-value fodder despite their strong fiber potential. This study evaluates PALF–cotton and PALF–polyester yarns, produced via conventional ring spinning, against 20 Ne 100% cotton, assessing key Uster® parameters including unevenness, CVm%, hairiness, defects, and elongation. The 100% cotton yarn demonstrated the highest uniformity (U% = 8.63) and minimal defect incidence, while blends particularly cotton–PALF exhibited greater irregularities (U% = 12.24). Nevertheless, elongation properties improved markedly in blends (8.53% for cotton–PALF; 9.66% for polyester–PALF vs. 5.83% for cotton) with hairiness maintained within acceptable thresholds. The results, analyzed through Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) using the SU1510 model from Japan, underscored PALF’s strategic role in enabling zero-waste manufacturing, upcycling agricultural residues into premium textile products, and advancing Bangladesh’s fiber independence under a sustainable production model.
Keyword: Sustainable, Pineapple Leaf Fiber (PALF), Biodegradability, zero-waste









Georgia Reader Reply
Et rerum totam nisi. Molestiae vel quam dolorum vel voluptatem et et. Est ad aut sapiente quis molestiae est qui cum soluta. Vero aut rerum vel. Rerum quos laboriosam placeat ex qui. Sint qui facilis et.